
Solar Energy
Solar power is the conversion of sunlight into electricity, either directly using
photovoltaics (PV), which convert light into electric current, or indirectly using
concentrated solar power (CSP), which use lenses or mirrors and tracking systems to focus a large area of sunlight into a small beam. Solar power is one of the cleanest, most abundant forms of energy. It emits zero greenhouse gases or other pollutants, uses no water, produces no waste and offers significant potential for short- and long-term
climate change
mitigation. Even though solar energy generation still only represents a small fraction of total energy comsumption, markets for solar technologies are growing rapidly, the cost of solar technologies have been significantly decreasing and technical advances and supportive public policies continue to offer the potential for additional cost reductions.
The rate at which solar energy is intercepted by the Earth is about 10,000 times greater than the rate at which humankind consumes energy
and although not all countries are equally endowed with solar energy, a significant contribution to the energy mix from direct solar energy is possible for virtually every country. Solar energy conversion consists of a large family of different technologies capable of meeting a variety of energy service needs for both developing and developed countries. Solar technologies can deliver heat, cooling, natural lighting, electricity, and fuels for a host of applications, but without the pollution!
Learn more.
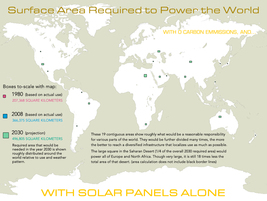
Credit: Land Art Generator Initiative | Click to enlarge
“I have no doubt that we will be successful in harnessing the sun's energy... If sunbeams were weapons of war, we would have had solar energy centuries ago.” ~ Sir George Porter, 1967 Nobel Prize Chemist
| |
"Getting 20 percent of our energy from renewable sources by 2020 would create 820,000 new jobs from renewable energy development, $66.7 billion in new capital investment, $25.6 billion in income to farmers, ranchers, and rural landowners, $2 billion in new local tax revenues, $10.5 billion in lower electricity and natural gas bills by 2020 (growing to $31.8 billion by 2030) and reductions in global warming pollution equal to taking 36.4 million cars off the road. Renewable energy savings equivalent to 15% of electricity consumption and 10% of natural gas consumption by 2020 could save $26 billion in consumer costs, eliminate 300 million tons of carbon emissions, reduce the need for 443 new 300 MW power plants and power 40 million homes In sum, we can face the challenge posed by global warming by taking steps today towards unleashing a clean energy future." ~ Sierra Club: Clean Energy Solutions - Renewable Energy
Advantages Of Solar Energy
- Sunlight is free, easily-accessible, inexhaustible! No
mountain-tops have to be blown up
or
ocean floors dug up.
- Unlike conventional fossil fuels, such as coal, oil and natural gas, solar power emits no polluting emissions, including those that cause global warming and degrade the health of nearby communities, ecosystems and wildlife. Discover the Effects of Pollution
- Solar power uses no water. On the flip side, a typical 500-megawatt coal-fired power plant draws about 2.2 billion gallons of water each year from nearby water bodies and as much as 75 trillion gallons of water is wasted on dirty energy each year.
- Solar power produces no waste. A single coal plant, on the other hand, typically creates more than 125,000 tons of ash and 193,000 tons of sludge from the smokestack scrubber each year and produces other toxic substances, including arsenic, mercury, chromium, and cadmium, which can contaminate drinking water supplies, damage vital human organs and the nervous system and severely or permanently damage ecosystems. Learn more.
- Solar power can slash utility bills for both residential and commercial consumers. Organic farmers in New Jersey installed solar panels in a former pasture and saw their monthly electric bill plunge from $1,500 to $2 and with a surplus of more than 500 kilowatts going into their first winter with the system! Learn more.
- Solar energy conserves natural resources for future generations.
- With no moving parts, solar panels are silent, easy to operate and rarely require maintenance.
- Because solar systems are highly reliable, require little maintenance and are ideal in distant or isolated places, solar energy has been the power supply choice for many industrial applications. Learn more.
- Solar panels can help utilities avoid blackouts by generating extra energy when demand for electricity is high, such as in the summertime, rather than fire up expensive and polluting "peak" power plants that otherwise lie dormant.
- Solar power has the potential to create hundreds of thousands of American high-earning, high-tech green jobs that don't pose the type of toxic, dangerous environments coal miners face.
Learn more.
- Solar power helps retain energy independence by reducing our dependence on foreign fossil fuels, particularly from unstable regions in the world, such as the Middle East, which can cause dramatic and unpredictable energy price hikes.
- Solar power offers significant potential for near- and long-term climate change mitigation since it does not emit greenhouse gases, which trap more heat and warm the planet. On the contrary, the extraction and burning of fossil fuels is fueling global warming and causing climate change.
- Solar power is transforming the lives of millions, especially in developing countries where sunsets would usually mean unrelenting darkness until sunrise or whose only sources of energy or light, such as kerosene lamps or leaky stoves burning biomass and coal, was a major source of indoor air pollution. However, with solar power, from small lanterns to photovoltaic panels, more people can now safely and efficiently light up the dark either indoors or out and have clean, sustainable electricity to power their lives. Learn more.
- Solar is providing a high number of good-paying, green jobs all over the U.S. and world. As Jeff Spross from Climate Progress states, "California, the state that the Hollywood film industry calls home, can boast 43,700 paying jobs in the solar industry in 2012, versus only 32,300 paid actors. Texas clocked in with 3,200 solar jobs, in comparison to the state’s 270 to 2,410 ranchers. And across the entire nation, 119,000 Americans were employed by the solar industry in 2012, versus only 87,500 by the coal mining industry." View the 2012 National Solar Jobs Census | View US State Solar Jobs Interactive Map
Where
And How Can Solar Energy Be Used?
Solar energy can be used anywhere the sun shines! Whether for residential areas, commercial buildings, industrial purposes, remote locations or for a variety of other applications, the power of the sun can be harnessed virtually anywhere and for a growing array of diverse purposes. Homeowners, farms and businesses across the country are installing solar water heaters and panels to reduce their electric bills.
Solar energy is also frequently used for transportation signaling, such as offshore navigation buoys, lighthouses, aircraft warning light structures, and increasingly in road traffic warning signals and street lighting. From powering environmental monitoring equipment and corrosion protection systems for pipelines, well-heads, bridges, and other structures to pumping water in remote areas as part of a portable water supply system, solar energy has few bounds to it's growing utilization of the sun. Specialized solar water pumps can even be designed for submersible use or to float on open water and large-scale desalination plants can also be PV powered using an array of PV modules with battery storage.
Learn more.
Furthermore,
solar power is transforming the lives of millions, especially in developing countries
where sunsets would usually mean unrelenting darkness until sunrise or
whose only sources of energy or light, such as kerosene lamps or leaky stoves burning biomass and coal, was a major source of indoor air pollution
(see also). However, with solar power, from small lanterns to photovoltaic panels,
more people can now safely and efficiently light up the dark
either indoors or out and have clean, sustainable electricity to power their lives.
Learn more.
Discover SolarCity, the largest solar installer in the US, famous for not selling, but leasing solar systems for monthly payments that are designed to be lower than what customers currently pay for their utility. This allows for customers to get solar systems on their roofs without spending tens of thousands of dollars upfront. Three ways to bring solar to the masses.
Discover SolarCity, the largest solar installer in the US, famous for not selling, but leasing solar systems for monthly payments that are designed to be lower than what customers currently pay for their utility. This allows for customers to get solar systems on their roofs without spending tens of thousands of dollars upfront. Three ways to bring solar to the masses.
Organic farmers in New Jersey installed solar panels in a former pasture and saw their monthly electric bill plunge from $1,500 to $2 and with a surplus of more than 500 kilowatts
going into their first winter with the system!
How Much Does Solar Energy Cost?

Source: Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory | Click to enlarge
The unsubsidized cost of renewable power produced from solar and wind energy will be
no more expensive than that from oil, natural gas, and coal by the end of the decade
(see also)
and
even less expensive thereafter. However, if you take into account the
very real health and environmental damage from fossil fuels,
wind and solar power is the least expensive energy sources worldwide.
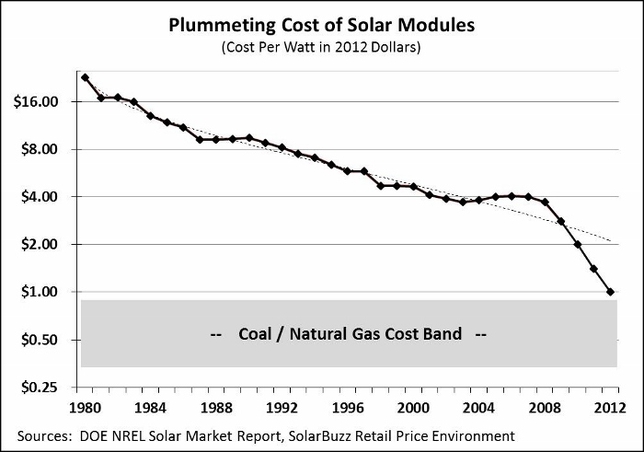
Credit: U.S. DOE | Click to enlarge
According to the
Natural Resources Defense Council, "The cost of solar energy has fallen sharply over the last 20 years, with accelerating price declines in the last 5 years. Still, electricity from a concentrated solar power plant can cost about 10 to 14 cents per kilowatt-hour, compared with about 4 cents per kilowatt-hour from a coal or natural gas power plant, but these prices should continue to drop thanks to falling installation costs, accessible, low-cost, long-term financing, and a healthy number of incentives and tax packages offered by nearly every state government. The current federal incentives include a 30 percent investment tax credit (ITC) and a five-year modified accelerated cost recovery system (MACRS), which allows system owners to deduct federal taxes on an accelerated timetable of system value depreciation. Experts predict the cost of solar power will drop below retail electricity rates in many parts of the country between 2013 and 2018 and to about 5 cents per kilowatt-hour by 2020."
In 2011, the
International Energy Agency stated, "The development of affordable, inexhaustible and clean solar energy technologies will have huge longer-term benefits. It will increase countries’ energy security through reliance on an indigenous, inexhaustible and mostly import-independent resource, enhance sustainability, reduce pollution, lower the costs of mitigating climate change, and keep fossil fuel prices lower than otherwise. These advantages are global. Hence the additional costs of the incentives for early deployment should be considered learning investments; they must be wisely spent and need to be widely shared."
State By State Solar Energy Incentive Programs
“The use of solar energy has not been opened up because the oil industry does not own the sun.” ~ Ralph Nader, Time Magazine 100 Most Influential Americans in the Twentieth Century
"In the business-as-usual scenario, electricity supply costs will nearly double by 2020. Unchecked growth in energy demand increases in fossil fuel prices and the cost of CO₂ emissions result in total electricity supply costs rising from today’s $2,300 billion US dollars per year to more than $4,000 billion in 2020, and $8,800 billion by 2050. By moving away from fossil fuels and reducing carbon emissions, we can stabilise energy costs for consumers. Between 2015 and 2020, most renewable energy sources will become cheaper than coal." ~ Greenpeace, The Energy [R]evolution
"It is time for a sustainable energy policy which puts consumers, the environment, human health, and peace first." ~ Dennis Kucinich, U.S. Congressman







